In this post we are going to take a closer look on what are the current phishing tactics employed in the wild. The trends uncovered by analyzing our new data-set of 5000 recents phishing sites will change the way you think about phishing. One of my current research project, with Jing and a bunch of people of the university of Michigan, is to develop an in-browser defense against phishing, that will be able to detect phishing sites as quickly as they are created. Instead of relying on a black list, it will use vision and machine learning algorithms. Before to set out on a journey to find the best way to do this, we needed to understand why detecting phishing sites is so difficult. There is little information on how phishers operate in the wild so we ran our own experiment and analyzed around 5000 recent phishing websites. Turnout that the results of this preliminary analysis are interesting by themselves and shed a new light on current phishers behaviors so I decided to share them with you via this blog post.
Methodology
Before delving into the results, let me explain how we got to them. First we collected, phishing urls via Phishtank which is the best resources to get phishing URLs. Next we used these URLs to feed our crawler, which took a screenshot and collected a bunch of information for each of these sites. Then we used Amazon Mechanical Turk (as usual :)) to have human review each screenshot and augment our data-set with “human intelligence”. To make sure our data-set is clean, we had every phishing site screenshot analyzed by three different Turkers. Finally we processed the data reported by the Turkers to compute the results that we are going to discuss. In particular we discarded meaningless results and used a voting system to come-up with a stable data set. In then end, we ended-up having data about 1000 phishing websites. It might not seems a lot of works but trust me, it took us a lot of effort to get there.
Type of Phishing
There is two kind of phishing websites: fake sites and scam sites. Fake sites are phishing sites that clone the appearance of the targeted website in the hope you will confuse the two and enter your credentials (login and password). Here is an example of a Paypal phishing site.
Paypal Fake website
Scam site try to talk you into entering your credentials for a dubious reason or another. The screenshot below show a phishing site that attempts to steal your MSN credentials via offering you a software that allows you to know who blocked you. Notice how the phisher, make clear that this is safe to use it .
MSN Credential phishing via a SCAM
Accordingly the first question that comes to mind is which is the favority phishier tactic ? Faking or Scamming ? Well it is about equal (48.2%, 51.8%) as visible in the graph below:

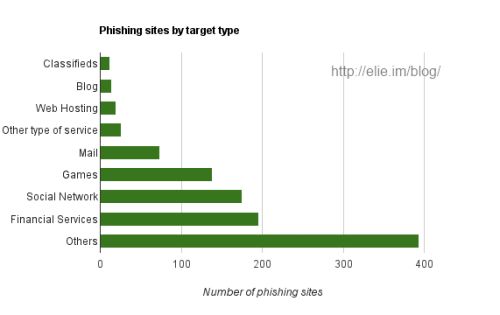
Phishing Sites Target Type
The next question is what kind of sites phishers are targeting ? Are they trying to steal your bank account, your email, or your Facebook account ? As visible on the chart below, for those we were able to categorize, Without any surprise financial services, like Paypal and Banks, are the most targeted. The next big target (no surprise here either) are social networks (Facebook, Orkut). What is surprising is that the third big type of target, are online games (World of Warcraft in particular) not email accounts. One hypothesis, that explains this trend is that reselling stolen online goods is a lucrative business.
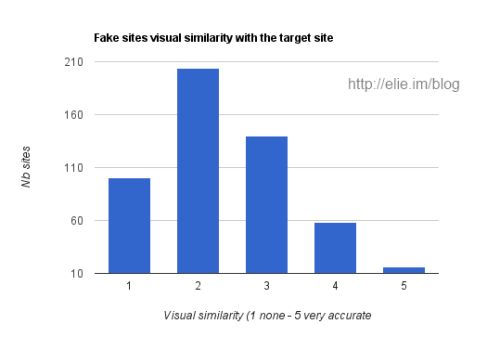
Visual Similarity
One other question, we asked Turkers is to rank how visually similar fakes sites are to the target site they attempt to phish. We asked to rank the fake phishing site on a scale from 1 to 5. 1 being completely different to 5 being close to a perfect copy. I was expecting to have a majority of sites to look very similar to their target. Oh boy, how wrong was I, as visible in the chart below in reality most fake sites are poorly executed (on purpose to avoid detection ?).
Here are some examples of phishing sites with different level of visual similarity:
- Eve-online phishing site (similarity 5/5 high resemblance)
- World of Warcraft phishing site (similarity 5/5 very similar)
- World of Warcraft phishing site (visual similarity 2/5 very few common point with the original site)
Why Detecting Phishing is Hard ?
So why detecting phishing is hard ? Well the results of our analysis suggest at least two reasons: First many phishing sites (51.8%) are scam sites not fake sites which make them harder to classify because we don’t have a baseline for them (the real site). The second explanation is that those who attempt to fake a realsite are poorly executed and therefore are hard to recognize. While I still believe that machine learning and vision algorithm can yield something (there are previous successful works on this), it is clear that we will need new ideas to deal with scam phishing sites and poorly executed fake sites. Right now, I am thinking using image content extraction and spacial correlation but only time will tell if it will work. There is also probably more to the data that what I discussed, so if you have an idea let me know. Thanks for reading this post. If you like it please sharing it with the world, it makes me happy You can follow me on Twitter @elie or on Google+




